Data Lifecycle Management (DLM) : A New Way Of Managing Data
In this digital age, generating data is no longer a problem. In fact, we're producing more data than ever. The main problem companies face is managing the data adequately. Do you always find it difficult to manage data and derive information? Then consider using Data Lifecycle Management or DLM. DLM allows you to manage the data flow from generation to erasure.

What Is DLM?
Data Lifecycle Management refers to the policy-drive approach to data handling. You define rules and policies that would apply to the data so that the data doesn't lose its integrity.
When data enter into the management system, it should follow the definition and structuring that's in place. The policies remain throughout the lifecycle of the data.
In practice, it is represented by a series of steps that start with data collection to data deletion. In some cases, it's extended to data re-use. DLM plays a critical role in automation and overall business operation.
Three Main Goals Of Data Lifecycle Management
If you're implementing DLM within your organization, you should do it with a goal in mind. In essence, Data Lifecycle Management can help you meet the three business goals mentioned below:
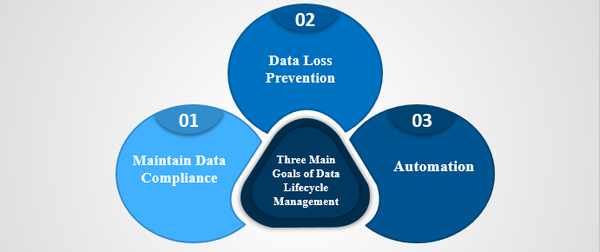
1. Maintain Data Compliance:
Several industries like healthcare, insurance, law, finance have strict regulations towards handling data. The use of DLM ensures your company stays in compliance with the laws and regulations required for your industry. GDPR and HIPAA (specifically for health insurance) are two of the most prominent data protection regulatory requirements. You need to design your DLM architecture according to these requirements.
2. Data Loss Prevention :
DLM defines how data should be processed, stored, and shared across the organization. Along with that, it lays out the practices for data backup, both at a local and off-site level. This prevents data loss to unexpected events like security breaches and outages.
3. Automation:
You can automate several of your business processes with DLM. Since automation is a top agenda for most businesses, irrespective of the sector, implementation of Data Lifecycle Management will help greatly. You need to implement smart policies that will oversee the lifecycle of data without much manual intervention. This would open up the door for automation.
Depending In your sector, your goals might be different for DLM. If designed and implemented smartly, you can meet those goals.
What are the Stages of Data Life Cycle Management?
Data Lifecycle Management consists of five stages. The data once entered into the management system goes through each of these stages. The five stages are
- Creation
- Storage
- Usage
- Archival
- Destruction
- Let's explore the stages in brief
1. Data Creation
In the first stage of DLM, the focus is on data creation. All the data you find in the system is created somewhere. It might be personal drives, on social media, on a text file in an unstructured way. DLM defines guidelines and policies for how the data is created and collected.
Defined in another way, data creation consists of two sub-processes: capture and acquisition. Covered in the creation policies are the following:
- Data types
- Sensitivity of data (private, public, restricted)
- Where they're used
- What they're used for
- Users who can use them
2. Data Storage
The next stage is concerned with storing the data that's collected. The best practices in IT have it that data should be stored in such a way that there is no single point of failure. There should be security strategies in place so that they can't be easily altered.
Where you store the data is also important. Depending on your local laws, you may be restricted to storing within your country to stay in compliance with local laws.
Along with storage, you'd also have to define recovery and backup plans.
3. Data Usage
The stored data will be used at some point in time. In the next stage, DLM defines who can use what types of data. If you've set up the previous two stages correctly, then setting up this stage will be relatively straightforward.
But if you're implementing DLM for automation, then creating policies can frameworks can be a complicated affair. The requirement to share and authorize data usage will change.
In such cases, you need to consider the value of data, to make correct decisions. You'd also have to plan about the second-order and processed data.
Along with data usage, think of data sharing. Data is often shared across the board and even with the outside world. This puts a risk on data for being breached or compromised. So you should have data sharing policies in place.
DLM is very strict when it comes to data sharing. You'd have to define very precise protocols for sharing central data among employees, users, customers, and third-party vendors.
4. Data Archival
After data is used, you have two options. One is to archive it or, two, destroy it forever. The decision is based on several factors, the importance of which is the usefulness and sensitivity of data.
Will Do you need the data in the future and it isn't sensitive? Then probably you should archive it. If you don't need it and it's very sensitive, it's better to delete it.
As a general rule, data should always be archived before being destroyed. DLM defines when, where, and for what length of time you need to archive the data.
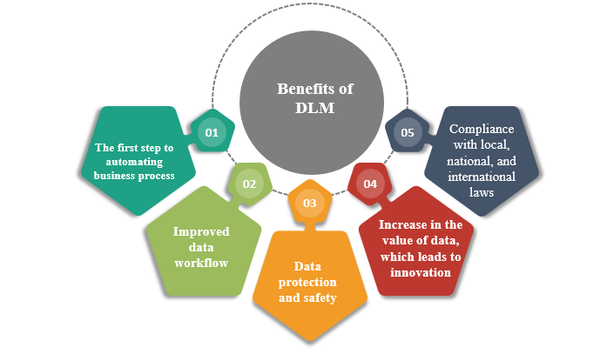
Benefits Of DLM
With that said, why take the pain of implementing Data Lifecycle Management? Here are some of the top benefits:
DLM is still in its infancy. You might have different terminologies. So, instead of data destruction, some publications may refer to it as data cleaning. They all mean the same thing. So for bettering the data within your organization, implement Data Lifecycle Management at the earliest.




