Agile Project Planning Template: The Key To Delivering Success Faster
What Is Agile Planning?
Agile planning is a project management methodology that emphasizes adaptability, collaboration, and continuous improvement throughout the project lifecycle. It is based on the principles laid out in the Agile Manifesto, which values individuals and interactions over processes and tools, working software over comprehensive documentation, customer collaboration over contract negotiation, and responding to change over following a plan.
4 Essential Characteristics of Agile Planning
The agile planning process is an iterative and incremental approach to planning and managing projects. It is a flexible and responsive approach that can be adapted to the changing needs of a project. Planning is essential to the success of any software development project, but it is especially important in Agile because the product is delivered in small increments.
The agile planning process is based on four essential characteristics:
1. Iterative and Incremental: The agile planning process is based on the principle of iteration, which means that plans are developed in small steps, with each step building on the previous one. This allows for flexibility and responsiveness to change.
2. Flexible and Responsive: The agile planning process is designed to be flexible and responsive to change. It is based on the principle of constant feedback and constant adaptation.
3. Teams: The agile planning process is based on the principle of team involvement. All members of the team are involved in the planning process and have a shared responsibility for the success of the project.
4. Customer Focus: The agile planning process is based on the principle of customer focus. The customer is involved in the planning process from the beginning, and their needs and requirements are considered at every stage.

Agile Project Scheduling Process
Agile project management is an iterative and incremental approach to project management that emphasizes flexibility and collaboration. The agile project scheduling process is a way for project managers to schedule and track agile projects.
The agile project scheduling process is composed of four steps: release planning, iteration planning, daily stand-ups, and retrospectives.
1. Release Planning: Release planning is the first step in the agile project scheduling process. In release planning, the project manager creates a high-level plan for the project. This plan includes the overall scope of the project, the project timeline, and the main deliverables.
2. Iteration Planning: Iteration planning is the second step in the agile project scheduling process. In iteration planning, the project manager creates a detailed plan for each iteration of the project. This plan includes the tasks that need to be completed in each iteration, the assignees for each task, and the timeline for each task.
3. Daily stand-ups: Daily stand-ups are the third step in the agile project scheduling process. Daily stand-ups are brief meetings in which the project manager and the team members discuss the progress of the project.
4. Agile Project Scheduling: The fourth and final step in the agile project scheduling process is retrospectives. Retrospectives are meetings in which the project manager and the team members reflect on the project and discuss what went well and what could be improved.

Benefits of Agile Project Plan
Let's delve into the benefits of Agile project planning:
1. Enhanced Flexibility: One of the key advantages of Agile project planning is its flexibility. Agile methodology allows for continuous iteration and improvement based on feedback received throughout the project lifecycle.
2. Improved Communication: Agile project planning promotes regular communication among team members, stakeholders, and clients. Daily stand-up meetings, sprint reviews, and retrospectives facilitate transparent communication, fostering a collaborative environment where everyone is on the same page.
3. Increased Customer Satisfaction: By embracing Agile project planning, teams can prioritize customer satisfaction by delivering incremental value in short iterations. Clients have the opportunity to provide feedback regularly, ensuring that the end product meets their expectations.
4. Efficient Resource Utilization: Agile project planning optimizes resource utilization by breaking down the project into smaller, manageable tasks known as user stories. This allows teams to focus on high-priority items first and allocate resources effectively.
5. Adaptability to Changes: In today's dynamic business environment, change is inevitable. Agile project planning embraces change and treats it as an opportunity for improvement. By incorporating feedback and adapting to evolving requirements, Agile teams can respond quickly to market shifts or emerging trends.
What Is Agile Project Management?
Agile is new norm of the industry and everyone in the tech industry is moving to agile. These set of tutorials and templates will help a scrum master or project manager to adopt agile. Agile is a methodology for the management of software project development. In contrast to a traditional sequential approach to software development, Agile focuses on the development of a series of incremental iterations of the product, each of which is functional and potentially can be deployed.
Agile Project Team Members
Agile Project Team Members play an important role in Agile Project Management:
1. Product Owner: The product owner plays a crucial role in agile project management by representing the voice of the customer and stakeholders. Their primary responsibility is to prioritize the product backlog, define the project vision, and make key decisions on what features should be included in the product. The product owner works closely with the development team to ensure that the product meets the needs of the end-users and delivers value.
2. Scrum Master: The scrum master is responsible for facilitating the agile process and ensuring that the team follows agile principles and practices. They act as a coach and mentor to the team, helping them overcome challenges and improve their performance. The scrum master also facilitates the daily stand-up meetings, sprint planning, review, and retrospective meetings to keep the team focused and aligned on project goals.
3. Development Team: The development team consists of cross-functional members with the skills and expertise needed to deliver the project deliverables. Team members collaborate closely to design, develop, test, and deliver working increments of the product in short iterations called sprints. The development team is self-organizing and responsible for estimating the effort required for each task and delivering high-quality work within the sprint timeframe.
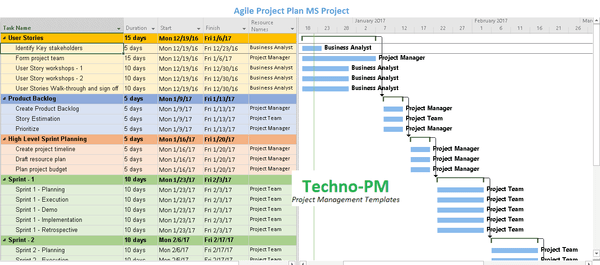
Agile Project Plan Excel Template
The project plan template in Excel and MS Project can be used for any general software development project run in an agile fashion. The project plan has the following high-level phases - User Stories, Product Backlog, High-Level Sprint Planning, actual Sprints, and Project Close. Under the user stories, the tasks are to identify key stakeholders, form a project team, conduct workshops, and then finally walk through the user stories.
Then we move on to finalizing the product backlog. Finalizing the product backlog involves creating the backlog and estimating the items, a.k.a PBI (Product Backlog Items). Once the backlog is ready, then the product owner and prioritizes the items in the backlog. Once the backlog is in place, we move on to planning sprints, and for each of the sprints, we look at resourcing, scope, or timeline and then also look at the budget.
For each of the sprints, we will plan when we will do the Sprint planning, actual work in the sprints, a demo date in which the team will showcase the work done. Once the team is ready to deploy the code built, we then plan the implementation. Finally a sprint review and retrospective to under what went well and what we should change. The project's last step is to close the project by conducting a project review and lessons learned report.
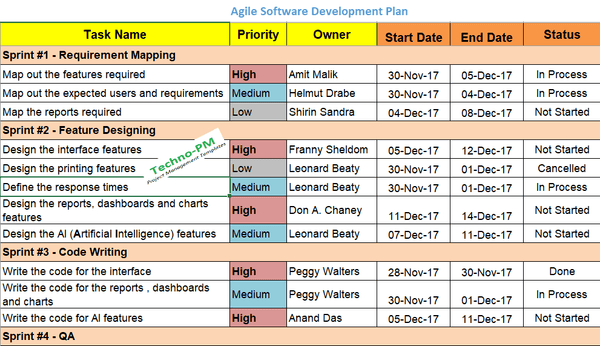
Agile Software Development Project Plan
The Software Development Project Plan is managed in an excel file and has information regarding each task's start/end dates, its priority, owner and status, and comments. The tasks are split up into 5 sprints, where each one has similar characteristics. These phases are – Requirement Mapping, Feature Designing, Code Writing, Quality Assurance, and User Testing.
The requirement mapping phase maps out the project's overall needs, which features it will include, and which problem it aims at solving for the client. The feature designing phase explains which features will be included in the project's final result, concerning the interface, reporting, AI (Artificial Intelligence), etc., and the users' response time. Feature design includes all the features mapped out in the previous phase that need to be coded, and this phase handles that.
In the code writing phase, the code is written according to the features' characterization in the previous phase. The written code needs to pass an elementary quality threshold, and this phase defines that threshold and makes sure that the code stands up to that standard. User Testing involves providing feedback for the coding team. This feedback will map out the fixes and new features that are required.
Agile Website Development Project Plan
The website plan is managed in an excel file and has information regarding each task's start/end dates, its priority, owner and status, and comments. The tasks are split up into 5 sprints, where each one has similar characteristics. These phases are – Look & Feel, Infrastructure, Site UX (User Experience), Coding, and Beta Testing.
The look & Feel phase sets each site's basic parameters: The font size, positioning of the pictures and written content, banner size, links placement, pop-ups, etc. The first task is the site mock-up, and this shows the potential users how the site will appear once completed. The infrastructure phase consists of the site's configuration on the servers of the company/clients, setting the domain of the site, and all activities that have to do with the site’s platform.
THE site UX (User Experience) phase sets the stage regarding the site's potential users will see and how their interaction with the site will be. It defines the required response times (For example, 0.3 seconds to transition to a new page once the user clicks on a link) and the testing parameters used internally for the initial testing sequences.
The coding phase outlines how the code will be written, which features will exist on the site and how it will be tested. During Beta Testing, the site is deemed well enough for testing by users who had no part in the development process; it is released to a few choice users. This phase's tasks define how it will be done and how the data will be collected and analyzed.

Agile Website Project Plan
SAP Agile Project Plan Sample
The SAP project contains the projects’ planned tasks, along with their start & end dates, the owner, status and priority, and comments. The plan is split into six sprints; each one represents the different phases of implementing the new system. These sprints are – Impact analysis, Design and Build, Infrastructure, Change Management, and Data Migration.
The impact analysis phase maps out the requirements of the new system, who will be using it, and what their required permissions are and is aimed at resolving any issues that may come up with the transition to the new system. In the Design and Build phase, all of the specifications of the new system are mapped out and written out on storyboards, and the design of the system is completed.
Testing all of the specifications which were mapped out in the previous phase are tested in this one, as well as the connectivity to the legacy systems. The infrastructure phase is when the required hardware is purchased in this phase and sets up the environments for testing and production.
This phase manages the change in how things are done (the SOP - Standard Operating Procedures), maps out the super (first) users, and conducts training to diminish the objections. Data Migration is required once the system is set up. The information from the legacy system needs to be transferred. This phase manages that and includes writing the code of the SAP modules.

Agile Release Plan Template
The release plan is often called “Sprint Zero” because it occurs before any specific product needs to be delivered. This sprint is the basis for the sprints in the product’s lifecycle, and the initial plan is laid out in it. This allows the team members to focus on the release's goal, its features, and their start/end dates. Once these features are agreed upon, they are allocated to a sprint, and their goal is clearly stated.
If any of the features aren’t necessary or the team is unclear on how to implement them, they will be marked as “unplanned” in the “Sprint” column. In the plan, there is also a “Status” column. Each features’ status may be – Initialized: the feature is in the process of planning and has started to be worked on. Assigned: the feature is assigned to a team (not to a specific team member). Planned: the feature is currently unassigned but has a time-frame for being completed.
As with any agile plan, the release plan is prone to changes if new stories are added or existing ones are deleted. After the release plan is finalized and agreed upon, it will serve the team members and the project manager to track the completion of the features, sprints, and the entire project. It will also be a baseline timeline for the project and will be updated throughout its lifecycle. If any new stories or features are required after the product has been defined and the project began, they will be added to the release plan.

Agile Project Planning Process
The strength of using an agile project management approach is that it is effortless yet still produces amazing results. While you’ll definitely get better at it the more you use it, creating an agile project plan takes five simple steps:
1. Create the User Story: In the user story phase, you’re simply answering the question, “What does the user/customer want?” and doing so in the simplest way possible. Usually, the people with different roles in an agile project like a customer, the product owner, SMEs, and members from the agile development team are involved.
2. Story Estimation: With the story complete, it’s time to estimate the effort it will require in a session that should include the product owner and members of the development team. You can use “story points” to measure how much effort will be required to implement the project’s story.
3. Prioritize: Once you have several different stories for your team to choose from, you need to prioritize them. The whole team should be involved in this step, and you can complete it by simply having everyone assign the choices with a point and seeing which one gets the most votes. The stories or items are documented in the product backlog. Another method is called “MoSCoW” and stands for “Must. Should. Could. Won’t.” With this method, each potential story is assigned one of these four descriptors, making it pretty clear by the end of your meeting which ones should take priority.
4. Release the Plan: In agile project management, a “release” is when the higher-ranked stories are ranked by priority. Again, you want the whole team involved to see what the product owner and stakeholders want and what kind of timeline they’re working with. These two groups can then transfer the release plan to the development team and get feedback about their expectations.
5. Sprint Planning: Now it’s time to create those sprints we talked about earlier. Typically the teams have a Sprint Planning Meeting to go over the production backlog items. The development team chooses one of the high-priority stories, divides it into multiple tasks, and then assigns them. This sprint planning process is repeated for every story until team capacity is reached.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Agile project planning is a crucial aspect of successful project management in today's fast-paced and dynamic business environment. By embracing Agile methodologies, project managers can ensure flexibility, adaptability, and efficiency in their project planning process. It allows for continuous improvement and collaboration among team members, leading to better outcomes and customer satisfaction. To implement Agile project planning effectively in your organization, consider investing in training and resources to stay informed and up-to-date on the latest trends and best practices in Agile project management.




