Financial Dashboard | Improving Portfolio Management with a Financials Dashboard
Financial Dashboard
Even in its most basic format, a sound financial dashboard can be an invaluable tool for financial portfolio management. The dashboard can be used to track data over extended periods of time, identify trends, and project the impact of best- and worst-case scenarios. It can also help to identify opportunities. In this article, we’re going to explore some of the basics and offer ideas for taking your financial dashboards to the next level.

Financial Dashboard
What Is A Financial Dashboard
A financial dashboard is a valuable tool that can provide a visual comparison or analysis of various KPIs (key performance indicators). Basic dashboards use simple functions in Microsoft® Excel, while more complex dashboards may be generated by entering data into applications such as Tableau.
The visual presentation of information allows for trends to be more easily identified and provides a framework to make analysis easier. Financial dashboards can also be used to see information on a single page.
What Are Financial KPIs?
Financial KPIs, or Key Performance Indicators, are the key measurements or quantifiable data points reviewed to evaluate a company’s performance.
They can be used at a high level to determine if a business is a worthwhile investment, especially compared to other businesses in the same sector. On a more granular level, they can identify course corrections for strategic, operational, and financial efforts.
One important point to note is that some KPIs are considered lagging indicators or indicators of what has happened. Others are considered leading indicators of what is on the horizon. Both have value; however, it is important to know which type of indicator you are dealing with to properly evaluate the metrics.
Check out our PMO KPI Dashboard
Examples of KPIs include:
- Revenue (monthly, quarterly, annual)
- Gross Profit Margin
- Net Profit Margin
- Return on Equity (ROE)
- Current Ratio
- Quick Ratio
- Revenue per FTE (Full Time Employee)
- Revenue per Customer
- Inventory Turnover Rate
- Cash Flow
- Cash Burn
- Employee Turnover Ratio
Leading vs. Lagging Indicators
Put simply, leading indicators are typically related to efforts and initiatives in process, while lagging indicators are definitive markers of efforts and initiatives.
Said another way, leading indicators are difficult to put into a financial dashboard but indicate where a company is headed. Lagging indicators are easily measured and easily put into a dashboard but only show where a company has been. The past is not a predictor of the future, so lagging indicators are often a poor predictor of where a company is headed.
Financial KPIs In A Financial Dashboard
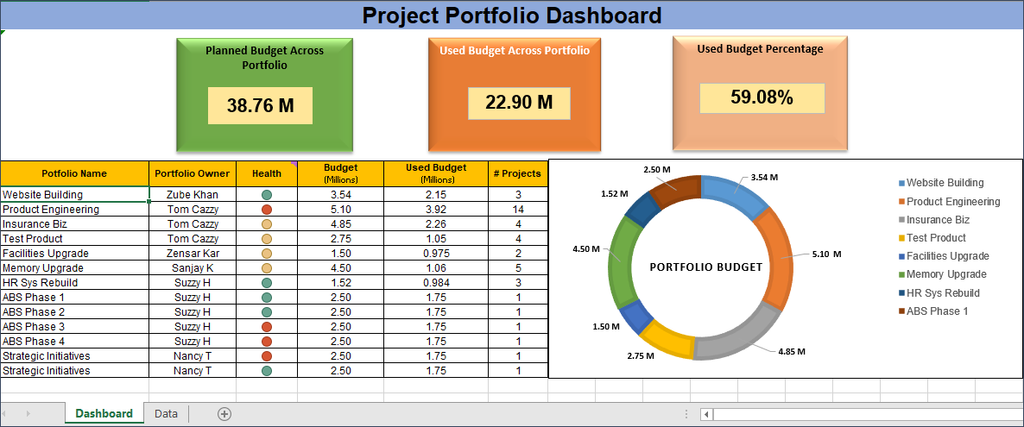
Financial Portfolio Management
The first step to building a good financial dashboard is identifying which KPIs to use. The choice of key performance indicators may vary depending on the entity’s industry.
An investor may want to see cash flow, net profit, quick ratio, current ratio, inventory turnover, or cash burn and may review the balance sheet for comparison against others and identify anomalies at a basic level. Elements such as employee turnover and retention, lifetime value of customers, or even foot traffic are harder to track down but can be good metrics for evaluating smaller businesses. Other metrics to consider adding to a financial dashboard include peer benchmarks and industry performance metrics.
While many of these are lagging indicators, when compared against industry overall, they do offer insight into how a company is faring against the competition.
Understanding Financial Metrics
When reviewing financial statements, the essential numbers that should be reviewed are called financial metrics. The balance sheet, the income statement, and the cash flow analysis (or statement) are the three best sources for these data points or metrics. The core metrics to identify are:
- Liquidity, which is shown on the Balance Sheet.
- Earnings or Net Income Growth, which comes from the Income Statement.
- Return on Assets, which is found by reviewing the Income Statement and Balance Sheet.
- Operating Cash Flow, which comes from the Cash Flow Analysis
Reviewing the financial metrics from the income statement, the cash flow, and the balance sheet can indicate how sound a company is and indicate whether it makes sense to invest in the company in the future.
Evaluating Financial Performance With A Financial Dashboard
To effectively evaluate financial performance, it is important to take an active role in monitoring investments. Having a high-level view makes it easier to optimize portfolio planning and ensures you’re focused on the right things. Ultimately you win by effectively responding to the data.
Best Practices Of Financial Dashboard
- Now that you’ve learned about what it is, why you should use one, and what it should measure, where do you start? These best practices will help you with that.
- Define your goal. You can’t figure out how to best use the data if you don’t clearly understand your goal.
- Consider the KPIs you will measure and determine the best layout when placing the page's data. Remember, the dashboard layout does not need to mimic the layout of the underlying data, and you have choices when determining how to view the data you choose to measure.
- Determine how you will source the data and how you will identify if trends are normal or abnormal. Identifying this will give you much-needed context to the data so that you can actually make smart decisions with the presented information.
- Keep it Simple. Keep simplicity top of mind. If you find yourself complicating the presentation of the data sourcing, stop and come up with a better plan. Simplicity wins. The more complicated you make it, the less likely it is to end up being useful. And you should never have to do more complications than the system you are using to understand the data presented.
- Choose your chart carefully. Choosing the wrong chart can destroy your efforts to present information, so be sure you understand which type of chart to use for what.
- Line charts display patterns of change. They are focused, simple, and precise. This type of chart format is common to most people, so it can easily aid decision-making.
- Bar charts allow for quick comparisons of items in the same category. They are also widely recognized and can be effective in their simplicity.
- Pie charts are seldom a good choice because they don’t accurately compare the information. They may be easy to view, but they don’t support sound decision making.
- Scatterplots are another method that lacks clarity and precision and doesn’t easily show relationships between numbers.
Dashboards Must Evolve
The most important point to consider is that your dashboard must evolve with the data and the changing goals. The information presented must not be static. If a goal changes, you may need to update a graph or even change the type of graph used.
Change is constant, and the most effective dashboards reflect a willingness to evolve.
Check out our other dashboard templates.
Improving Portfolio Management With A Financials Dashboard
The purpose of the financial dashboard, even the most basic type, is to support information review and decision making. By presenting an extended view of information, the dashboard can help identify trends and identify opportunities.
An effective data dashboard should be easy on the eye, simple, and visually balanced. By tailoring the presentation to your goals, you’ll find you create an effective dashboard that is useful well beyond the initial creation.





Leave a comment