Project Financial Planning
What is a Financial Plan?
A financial plan is a comprehensive evaluation of an individual's current pay and future financial state. The evaluation includes an individual's assets, liabilities, income, insurance, and taxes. Financial planning also includes the creation of a budget and the implementation of strategies to meet financial goals.
The goal of financial planning is to help an individual achieve financial security and independence. Financial planning is a process that should be revisited regularly to ensure that an individual's financial goals are on track.
It is important to have a financial plan in place as it can help keep personal finances on track and provide a road map for achieving financial goals. without a financial plan, it can be difficult to make investment decisions.
Why is a Financial Plan Important for Your Business?
The financial plan is a detailed road map that shows where your business is today, where it wants to be in the future, and how it will get there. The plan is important because it:
- Provides a clear picture of your business's financial health
- Sets financial goals and targets to strive for
- Creates a budget to track expenses and income
- Helps you identify potential financial risks and opportunities
- Helps you make informed decisions about where to invest your money
Creating a financial plan may seem like a daunting task, but it is essential for the success of your business. By taking the time to develop a financial plan, you will be putting your business on the path to financial stability and growth.
The Components of a Successful Financial Plan.
Creating a financial plan may seem like a daunting task, but it is essential for the success of your business. By taking the time to develop a financial plan, you will be putting your business on the path to financial stability and growth. There are a few different components that should be included in a financial plan. These components can be divided into three categories:
- Financial Statements: These include your income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement.
- Financial Ratios: Ratios provide a way to measure and compare different aspects of your business's financial health.
- Financial Projections: Projections show how your business's financial situation is expected to change in the future.
It is a detailed plan that outlines how you will achieve your financial goals. The components of a successful financial plan include:
- A clear and concise statement of your financial goals.
- A detailed budget that outlines your income and expenses.
- A savings plan that outlines how you will save for your future.
- An investment plan that outlines how you will invest your money.
- A retirement plan that outlines how you will support yourself in retirement.
- An insurance plan that protects you and your family in case of an unexpected event.
- A tax plan that minimizes your tax liability.
- An estate plan that ensures your assets are distributed according to your wishes.
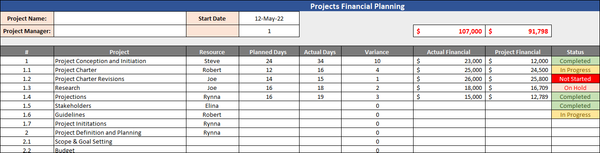
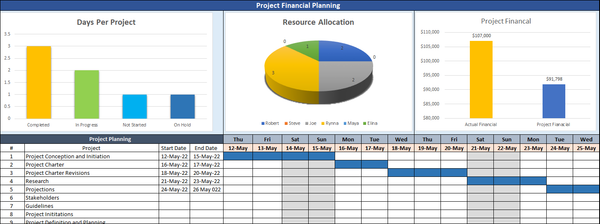
How to Create a Project Financial Plan?
As a project manager, you are responsible for ensuring that your project is completed on time, within budget, and to the required quality standards. To do this, you need to always have a clear understanding of the project’s financial position. This is where a project financial plan comes in.
A project financial plan is a document that outlines the expected revenues and expenses for a project over its lifespan. It is essential for project managers, as it provides them with a clear overview of the project’s financial health and allows them to identify potential problems early on.
We Will Explain in Detail How to Create a Project Financial Plan.
1. Define the Scope of the Project:
The first step in creating a financial plan is to define the scope of the project. This includes deciding what activities will be included in the project and what resources will be required. Once you have a clear understanding of the project’s scope, you can begin to estimate its costs.
2. Estimate the Costs of the Project:
The next step is to estimate the costs of the project. This includes all labor, material, and other costs that will be incurred during the project. Make sure to include both one-time and recurring costs in your estimate.
3. Forecast the Revenues for the Project:
Once you have estimated the costs of the project, you need to forecast its revenues. This involves estimating how much income will be generated from the sale of products or services associated with the project. It is important to be realistic when forecasting revenues, as this will impact your ability to achieve your financial goals for the project.
4. Create a Financial Model for the Project:
Once you have estimated the costs and revenues for the project, you can create a financial model. This will help you to see how the project’s costs and revenues interact over time. It is important to create a financial model that is realistic and achievable.
5. Make Assumptions About the Project:
Once you have created a financial model for the project, you need to make assumptions about its future. This includes estimating the rate of growth for the project and predicting how long it will take to achieve your financial goals. It is important to review your assumptions regularly to ensure that they are still accurate.
6. Evaluate the Results of Your Financial Plan:
After you have implemented your financial plan, you need to evaluate its results. This includes assessing whether you have achieved your financial goals for the project. If you have not achieved your goals, you may need to revise your plan.
The Benefits of the Project Financial Plan:
The benefits of the Project Financial Plan are:
- It provides a clear and concise financial picture of the project.
- It helps in identifying the key financial risks associated with the project.
- It aids in decision-making by providing a clear understanding of the cost implications of different project options.
- It facilitates better communication with project stakeholders by providing them with a detailed view of the project's financials.
- It strengthens the project's financial management by providing a clear framework for monitoring and controlling project expenditure.




