Risk Mitigation: A Comprehensive Guide
Every business face risks, some more than others. But regardless of the size or industry of your company, risk mitigation should be a key part of your business strategy. By taking proactive measures to identify and address potential risks, you can protect your business from financial losses, legal liabilities, and reputational damage. This guide provides an overview of risk mitigation, including the definition of risk mitigation, the benefits of mitigation, the types of risks faced by businesses, and the steps involved in creating a risk mitigation plan.
Defining Risk Mitigation :
Risk mitigation refers to the process of reducing or eliminating the potential impact of risks to an organization or project. The goal of risk mitigation is to identify potential risks, assess their impact and likelihood, and take steps to minimize or eliminate them.
Risk mitigation can take many forms, including risk avoidance, risk reduction, risk acceptance, risk transfer, and risk sharing, and each approach must be tailored to the specific risks an organization faces.
Effective risk mitigation strategies involve a continuous process of risk assessment, planning, implementation, monitoring, and revision to ensure that risks are effectively managed and minimized over time.
Some Common Risk Mitigation Techniques Are:
- Risk Avoidance: eliminating the possibility of a risk occurring. This can be achieved by not engaging in certain activities or by changing the project parameters to avoid risky situations.
- Risk Reduction: taking steps to reduce the probability of a risk occurring or its potential impact. For example, regularly backing up data to reduce the risk of data loss or implementing security protocols to reduce the risk of cyber-attacks.
- Risk Acceptance: acknowledging that a risk exists and accepting its potential impact. This may be the case if the cost or effort of controlling the risk outweighs its potential impact.
- Risk Transfer: transferring the risk to another party, often through insurance or contractual agreements.
- Risk Sharing: sharing the risk with another party, often through partnerships or joint ventures.
Why Is Risk Mitigation Important?
However, risk mitigation is important because it helps organizations anticipate potential risks and take proactive measures to reduce or eliminate their impact. By identifying and mitigating risks, organizations can avoid financial loss, reputational damage, and other negative consequences. Risk mitigation also helps organizations comply with legal and regulatory requirements and ensure organizational continuity.
Furthermore, risk mitigation strategies can improve the overall efficiency and effectiveness of organizational operations by identifying areas for improvement and implementing measures to mitigate associated risks. This can help organizations streamline processes, reduce costs, and improve the quality of their products or services. Additionally, risk mitigation can enhance stakeholder confidence and trust in the organization, leading to increased loyalty and support. Overall, risk mitigation is essential for maintaining the long-term resilience and sustainability of organizations.
The Benefits Of Risk Mitigation
- Minimizes Losses: Risk mitigation helps in reducing or minimizing the potential losses that could be incurred as a result of an unexpected event. This means that the impact of risks is reduced, thereby improving organizational resilience.
- Increased Confidence: Knowing that risks have been mitigated, successful mitigation efforts create more confidence in an organization. This is because taking steps to prepare your organization for the worst-case scenario demonstrates that you are serious and intentional about protecting the company's future.
- Improved Business Continuity: The mitigation of risks enables businesses to continue operating, even in the most challenging of situations. Defining and implementing policies and procedures helps ensure that a firm continues delivering goods and services, even if some risks and uncertainties do materialize.
- Reduced Costs: Risk mitigation helps to reduce the costs associated with unexpected events. By taking appropriate measures, resources, and other expenses required to mitigate the adverse effects risk events, and other contingencies can be reduced.
- Increased Competitive Advantage: A company that is capable of mitigating risks effectively is better equipped than its peers to handle crisis situations. This creates an advantage that adds to the business model and reputation, helping the company compete more effectively.
- Enables Smart Decision Making: A significant advantage of risk mitigation is that it facilitates informed decision-making. Well-informed members of the organization, stakeholders, and business leaders can use risk management to ascertain the potential impact of various choices and how these decisions may impact a firm's future growth and profit margins.
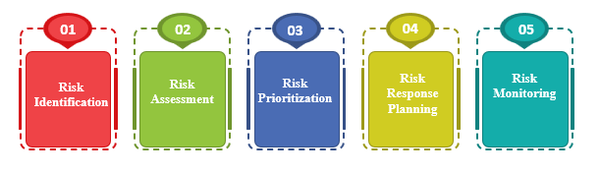
The Process Of Risk Mitigation :
- Risk Identification: The first step in risk mitigation is identifying potential risks. This can be done through brainstorming sessions, reviewing historical data, analysing industry trends, and consulting with stakeholders.
- Risk Assessment: Once the potential risks have been identified, the next step is to assess their probability and impact. This involves evaluating the likelihood of the risk occurring and the extent to which it could negatively impact the project, organization, or individual.
- Risk Prioritization: After assessing the risks, they need to be prioritized based on their potential impact and probability. This helps in determining which risks require immediate attention and which ones can be addressed later.
- Risk Response Planning: In this step, plans are developed to mitigate the risks. This may include avoiding the risk, transferring the risk to another party, mitigating the risk, or accepting the risk.
- Risk Monitoring: The risk mitigation process doesn't stop at planning. It is important to continually monitor the risks to ensure that the mitigation plans are effective. Regular monitoring helps to identify changes in the risk environment, and new risks may emerge, requiring updated mitigation plans.
Common Risk Mitigation Strategies :
- Risk Avoidance: Avoiding the risk altogether by not engaging in the activity that creates the risk.
- Risk Reduction: Taking actions to reduce the likelihood or impact of the risk, such as implementing safety measures or redundancies.
- Risk Transfer: Transferring the risk to another party, such as through insurance or outsourcing.
- Risk Acceptance: Accepting the risk and its potential consequences, while planning for ways to minimize damage.
- Contingency Planning: Planning for potential risks and creating an action plan to respond if they occur.
- Business Continuity Planning: Developing a plan for how the organization will continue to operate in the event of a risk or disaster.
- Crisis Management: Preparing for and managing potential crises to minimize their impact.
- Training and Education: Providing training and education to employees on how to identify and manage risks.
- Compliance: Ensuring the organization is meeting all legal and regulatory requirements to prevent legal and financial risks.
- Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: Continuously monitoring and assessing risks and improving risk management processes over time.
Conclusion :
In conclusion, risk mitigation is a critical process that helps organizations identify, assess, and control potential risks before they manifest into real problems. Organizations that prioritize risk mitigation enjoy the benefits of improved efficiency, enhanced reputation, and reduced costs of operations. To achieve a successful risk mitigation program, organizations need to adopt a comprehensive approach that involves identifying potential risks, prioritizing them by severity, developing mitigation strategies, and monitoring their effectiveness. Ultimately, implementing a robust risk mitigation plan helps organizations maximize their opportunities and navigate the complex business environment with confidence.




