Project Quality Management Processes + Techniques
Project Quality Management refers to the process of ensuring that a project meets the specific requirements or expectations of stakeholders. Quality management is important for any project, as it helps to ensure that the project objectives are met and that the final product or service meets the required quality standards. To achieve quality outcomes, project managers should plan, execute and control activities to control and measure the effectiveness and efficiency of project deliverables. This involves establishing quality objectives, defining quality requirements, and ensuring that quality is monitored throughout the project lifecycle. This topic explores the essential aspects of Project Quality Management, including the processes, tools, and techniques used to ensure that projects are completed successfully.
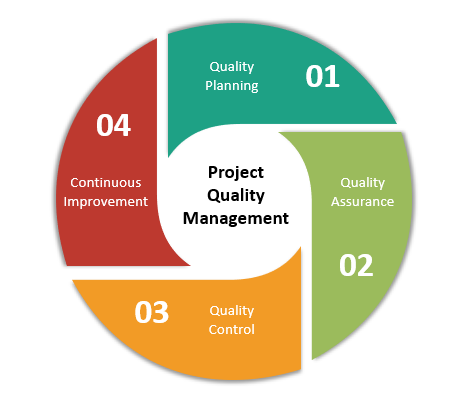
Understanding Project Quality Management
Project Quality Management is the process of ensuring that a project meets the required standards of quality. It involves the identification and definition of quality standards, the establishment of quality control processes, and the tracking and monitoring of quality throughout the project lifecycle.
- Quality Planning: This involves determining the quality standards that are required for a project, and determining how those standards will be achieved. Quality planning includes creating a quality management plan which outlines the quality objectives, attributes, and metrics that will be used to measure project performance.
- Quality Assurance: This involves ensuring that the quality standards are being met throughout the project. This is achieved through quality audits and inspections, which are conducted to assess the project's compliance with the established quality standards.
- Quality Control: This involves monitoring the project's quality and making changes as needed to ensure that the project meets the established quality standards. Quality control includes reviewing project deliverables, testing software, and hardware components, and validating project requirements.
- Continuous Improvement: This involves measuring and analyzing the project's performance to find areas for improvement. Continuous improvement involves using feedback from stakeholders and team members to identify areas for improvement and implementing changes to improve the project's quality.
Defining Quality Requirements
Quality requirements are the specific characteristics or features of a product or service that must be met to satisfy the needs and expectations of the customer or stakeholder. These requirements are often defined in terms of performance, reliability, usability, safety, maintainability, and other key factors that are important to the end user. The process of defining quality requirements involves a thorough understanding of the customer’s needs and expectations, as well as the technical and functional requirements of the product or service.
This requires careful analysis, planning, and communication to ensure that all stakeholders are on the same page and that the final product or service meets or exceeds expectations. Defining quality requirements is a critical step in the development process because it ensures that the result will meet the needs and expectations of the customer or stakeholder.
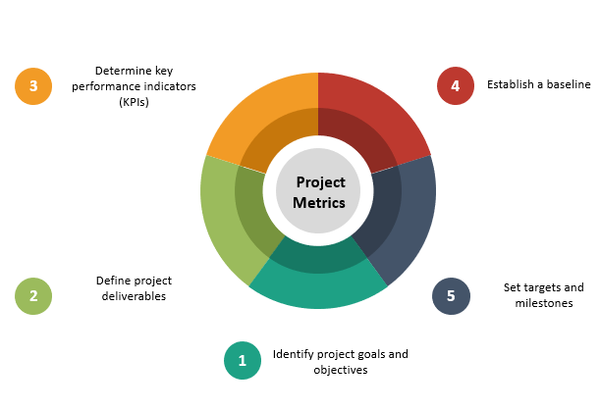
Developing Project Metrics
- Identify project goals and objectives: The first step to developing effective project metrics is to identify the goals and objectives of the project. These goals should be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) to ensure that they can be tracked and evaluated effectively.
- Define project deliverables: To determine the success of a project, it is essential to establish the deliverables or outputs that will be produced. This could include anything from completed tasks or milestones to final reports or products.
- Determine key performance indicators (KPIs): KPIs are the specific metrics that will be used to measure the success of the project. They should be tailored to the goals and objectives of the project and should be measurable and quantifiable.
- Establish a baseline: Before the project begins, establish a baseline for each identified KPI. This will serve as the starting point for tracking progress and evaluating success.
- Set targets and milestones: Set specific targets and milestones for each KPI. These targets should be realistic and achievable but also challenging enough to drive progress and motivate team members.
Quality Assurance vs Quality Control
Quality assurance is the process of planning, designing, and implementing systems and processes to ensure that products or services are consistently of high quality. It involves setting up procedures, processes, and training to reduce the risk of defects or errors in the production process. The focus of quality assurance is prevention, and it aims to ensure that defects do not occur in the first place.
Quality control, on the other hand, is the process of verifying that products or services meet customer requirements and are free of defects. It includes techniques like testing, inspection, and sampling to identify and address any discrepancies that may occur during the production process. The focus of quality control is detection, and it aims to ensure that defects are identified and corrected before the product reaches the customer.
In summary, while quality assurance is focused on preventing defects from occurring, quality control is focused on identifying and correcting defects that have already occurred. Both processes are important to maintain quality standards and ensure customer satisfaction.
Techniques to Ensure Quality Management
- Create a Quality Management Plan: A comprehensive quality management plan should be created that meets the requirements of the project and includes specific goals, defined processes, and measurable objectives.
- Implement Quality Assurance: Quality assurance involves identifying and addressing potential quality issues throughout the project life cycle. This includes monitoring and evaluating processes, identifying potential problems, and taking corrective actions before the issues become larger problems.
- Use Quality Control: Quality control tools and techniques are used to maintain the quality of the project deliverables. These may include inspection, testing, and auditing to verify that the project outputs meet the required specifications and standards.
- Continuous improvement: A continuous improvement process should be implemented to ensure that lessons learned from previous projects are incorporated into the quality management practices of current and future projects.
- Engage Stakeholders: Engaging stakeholders, including customers, sponsors, and team members, can provide valuable feedback on the quality of project outputs and can help identify areas for improvement.
- Training and Education: Ensuring that the project team members are trained and educated on the quality management processes are essential to maintain the desired quality levels of the project deliverables.
Continuously Improve your Quality Management Processes
- Identify and Prioritize areas for improvement: Conduct regular evaluations of your quality management processes to identify areas that need improvement. Prioritize areas that have the greatest impact on the overall quality of your products or services.
- Define and Measure Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Establish measurable KPIs to monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of your quality management processes. Regularly review these metrics and determine if they are still relevant or need to be updated.
- Implement Continuous Improvement Initiatives: Encourage employees to share their ideas for improving processes. Implement effective change management processes to introduce new processes, review feedback, and measure success.
- Evaluate and Train Employees: Evaluate employee skills and knowledge to ensure they have the training they need to reach high-quality standards. Continuous training and development programs help to keep employees updated and engaged.
Conclusion
In conclusion, project quality management is a vital aspect of project management. The goal is to deliver a project that meets or exceeds the client's expectations. A comprehensive understanding of project quality management processes and techniques is necessary to achieve this aim. The processes involved in project quality management include plan quality management, performing quality assurance, and controlling quality. These processes are interdependent and must be carried out systematically to achieve the desired outcome.




